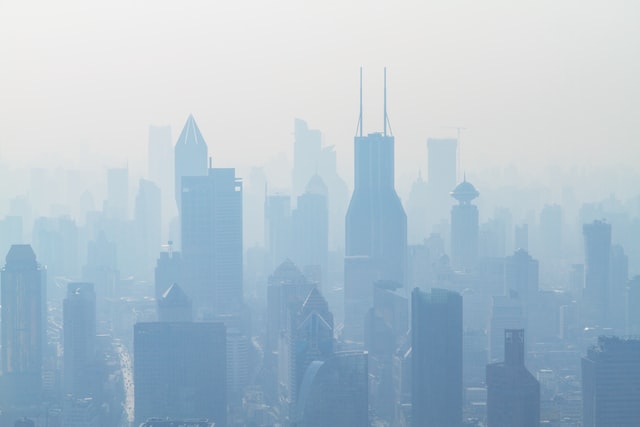
Air contamination significantly affects people’s health in large cities. In most regions, the benefits earned when cities improve air quality quickly erode due to the rapid population increase in urban areas. Factory emissions and the unrelenting traffic in urban centers often increase air contaminants in cities beyond the WHO recommended levels.
According to the World Health Organization, air pollution in cities is the most significant environmental health problem, killing millions of people annually. Almost one in every ten deaths annually occurs because of contaminants in the air.
More than 6,000 cities in 117 countries report their air quality measurements to the WHO. Of all city dwellers globally, only 17% live in cities that maintain the air quality level the WHO recommends. More than half of urban dwellers live in cities that exceed the recommended air pollution levels by 2.5 times.
The recommended safe limit for air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter is 20mcg/m3. In a city like Paris, the average level is 38mcg/m3. Beijing, one of the most polluted cities in the world, clocks in at over 300mcg/m3. The city lives with a perpetual orange alert.
Why is Air Quality such a Big Problem in Modern Cities?
Most cities that monitor air quality report that it is becoming worse. Factors such as reliance on coal-fired power plants, excessive personal vehicles, use of biomass for heating and cooking, and inefficient energy use in buildings contribute to increasing air pollution. Unfortunately, most people do not feel compelled to change their activities unless they become affected directly. Cities improve air quality by restricting people’s activity, but the public perceives it as an attack on their liberties. Here is why air quality should be a big deal for every city dweller.
Air pollution is creating a health crisis
Most people would agree with the WHO that air pollution is a global health emergency. It is a threat to everyone regardless of their social or economic status. The sources of air pollution can be very different on city streets and inside houses. However, their effects are similar no matter where you are. Air pollution causes asthma, respiratory illnesses, heart disease, lung cancer, pregnancy complications, etc. The most vulnerable people to air pollution include expectant mothers, infants, the elderly, and people with chronic health conditions.
Poor air quality negatively impacts the environment
Though people are more worried about how air pollution affects their health, it also impacts the environment. People living in cities feel the effects of air pollution. However, some air pollution contributes to widespread crises like global warming.
One of the less noticeable signs of air pollution is acid rain. It is a form of wet or dry precipitation containing toxic levels of sulfuric and nitric acid. This rain acidifies the soil and open water bodies, damages plants, corrodes buildings and outdoor sculptures, and damages buildings under construction.
Global warming keeps making headlines all over the world. Unfortunately, a significant portion of greenhouse gases comes from cities. The risk from global warming is rising and causing problems like food insecurity and the extinction of plants and animals. Unfortunately, global warming affects people disproportionately based on their economic status.
Air pollution affects visibility in cities
A very noticeable form of air pollution that makes cities improve air quality is haze. Haze reduces the transparency of air because it comprises suspended particles. The haze sources include vehicles, power plants, and industrial facilities.
Smog and soot
It is the most prevalent particulate matter pollution in cities. Smog, otherwise known as ground-level ozone, is a health concern for many people. Soot that enters the lungs can worsen bronchitis, cause heart attacks, and lead to premature deaths.
Poorer neighborhoods are at greater risk
People build facilities that cause substantial air pollution next to lower-income neighborhoods. It is an unfortunate coincidence because of the lower cost of land. Major highways also tend to pass through low-income locations. The people living in these places are therefore likely to suffer more due to air pollution in cities.

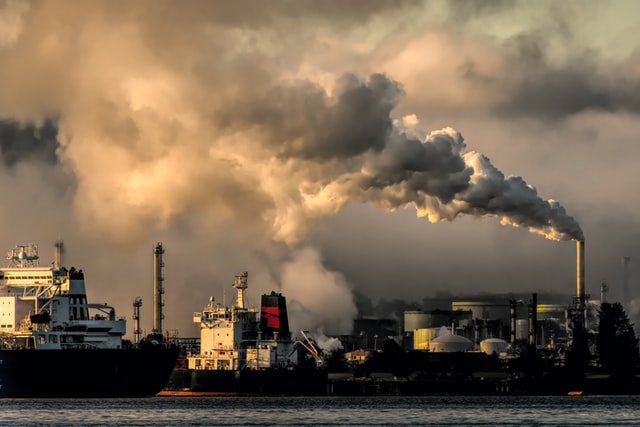
What can People do to Combat Poor Air Quality?
Many cities improve air quality by implementing blanket measures to control the activities of people and industries. However, people can contribute to improving air quality in their cities by doing the following:
Use public transport
When you use public transportation, you spend less money than driving your car. Public transport helps to reduce congestion and air pollution by extension.
Walk and cycle rather than drive
You produce zero emissions when you walk or ride a bicycle. You can significantly improve your health too. Many companies offer cheap bike rentals even if you don’t have a bike.
Ride-sharing and carpooling
If you are friends with someone who regularly drives to your destination, you can use one vehicle. This action can significantly ease congestion in cities and reduce air pollution. Some apps can help you to find carpool partners.
Use electric transportation
Fossil fuels are one of the reasons why cities improve air quality. Cars that use gas or diesel significantly contribute to air pollution in cities. If you buy an electric vehicle, you will reduce your emissions to zero and save money in the long run.
Buying local produce and products
Local products travel less. Therefore, you will be helping to reduce emissions from transportation when you buy them. You also regain control of what you eat because you know its source and how they make it.
Hosting air quality sensors
You could install a sensor for air quality on your premises. The sensor contributes air quality information to your fellow citizens and governments. These sensors use very little power.

How can Smart Technologies help to Improve Air Quality?
Monitoring remains one of the best ways to help cities manage air quality. Many cities have put air quality sensors on new infrastructure such as street lights. For instance, in 2014, Chicago installed a citywide sensor array on lampposts to monitor air quality. The city uses the data to predict air quality problems and take preventive action.
Other cities have innovative applications of technology that help them monitor their air quality. Over 65 cities in the world have Soofa benches. They are park benches with solar panels for charging devices via USB ports. In addition to these functions, they have built-in air quality sensors, temperature sensors, radiation sensors, and traffic sensors.
How are Smart Cities Improving Air Quality?
One of the most eye-opening consequences of the Covid-19 pandemic was its dramatic impact on air quality in cities globally. Predictably, the lifting of lockdown measures caused the pollution levels to return to pre-2019 levels. The issue of air quality still has a lot of media attention. Citizens are also pressuring politicians to introduce initiatives to guarantee cleaner air. One of the ways that cities are achieving the objective is using smart devices. The following are some of the ways cities improve air quality.
Increased use of mobile air quality sensors
Some cities attach air quality sensors to objects that move around the city. Cars are the preferred carriers of mobile sensors because they can traverse a town and quickly map out its air quality. Google partnered with the Environmental Defense Fund to put methane sensors on their street view cars. They helped to identify more than 4,000 gas leaks. Google installed a more robust air quality measuring system after partnering with Aclima’s Environmental Intelligence Platform. The sensors collected more than 150 million measurements after 750 driving hours. This data was enough to create a street-level air quality map across the city.
Collecting Better quality data
In the past, data about air quality came from one or two large monitoring stations. These stations had sophisticated equipment that could collect detailed information about the air in the vicinity. However, they were not very effective at measuring the air quality of the entire city.
The problem with the previous system was that air quality could vary significantly from one neighbourhood to the next. Therefore, the data collected by these large centres could not help cities improve air quality. Mobile monitoring technologies stepped in to fill in the data gap. Moreover, technological advancement has led to much smaller air quality sensors. Although they don’t collect as much data as their larger counterparts, cities can deploy numerous small sensors to paint the complete picture.
In 2014, an air quality measuring trial conducted in Dublin attached sensors to 30 bicycles in a bike-share program. The bikes gathered enough data to map out the air quality of the entire city in three days. Using bike share programs can significantly reduce the number of sensors required because one detector can replace numerous fixed sensors at a lower cost.
In 2016, the city of London, England, attached sensors to three pigeons and used them to collect air quality data for three days. The public could access real-time data about the air quality with a Twitter handle (@PigeonAir).
Conclusion
One of the best ways for cities to improve their residents’ quality of life is to push for cleaner air. Cities improve air quality using a variety of methods. The methods rely on accurate real-time data about pollutants in the air. Although the cost of air quality monitoring equipment has reduced significantly, the price could still be prohibitive for smaller cities.
If you want to learn more about smart cities, smart buildings, PropTech, and sustainability, feel free to take a look at our other articles